Welding is an essential skill in various industries, enabling the construction and maintenance of metal structures and machinery. However, it's not without its risks. Welding involves high temperatures, intense light, and hazardous fumes, making safety a top priority. Whether you're a seasoned professional or a beginner, understanding welding safety is crucial. This guide will delve into the hazards associated with welding, offer practical tips, and outline precautions to ensure a safe working environment.
I. Introduction to Welding Hazards
Welding hazards are numerous and varied, but they generally fall into several key categories: physical, chemical, electrical, and ergonomic.
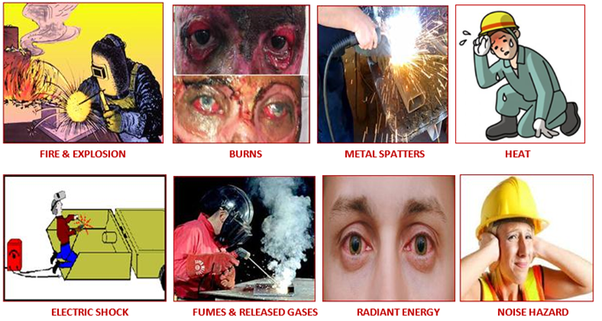
1) Physical Hazards:
Burns: The high temperatures generated by welding can cause severe burns. This is perhaps the most immediate and obvious danger.
Eye Damage: The intense light produced by welding arcs can cause arc eye or welder’s flash, a painful condition resulting from exposure to ultraviolet rays.
Radiation: Welders are exposed to ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation, which can cause skin burns and eye injuries.
Noise: Welding processes can produce high levels of noise, leading to hearing loss over time.
2) Chemical Hazards:
Fumes and Gases: Welding produces hazardous fumes and gases, including ozone, nitrogen oxides, and carbon monoxide, which can cause serious health issues when inhaled.
Toxic Metals: Metals like lead, cadmium, and chromium can be present in welding materials, posing additional health risks.
3) Electrical Hazards:
Electric Shock: Welding equipment uses high voltage, and contact with live electrical components can result in electric shock.
Electromagnetic Fields (EMFs): Prolonged exposure to EMFs generated by welding equipment may pose health risks, although more research is needed in this area.
4) Ergonomic Hazards:
Repetitive Stress Injuries: The repetitive nature of welding can lead to musculoskeletal disorders, especially in the hands, wrists, and back.
Postural Problems: Poor posture during welding tasks can result in long-term musculoskeletal issues.
II. Essential Welding Safety Tips
To mitigate these hazards, welders should adhere to a set of safety practices designed to protect their health and well-being.

1) Proper Training and Certification:
Training Programs: Ensure you have completed a comprehensive welding training program. This should cover safe welding practices, equipment handling, and emergency procedures.
Certification: Obtain certification from a recognized body, such as the American Welding Society (AWS). Certification ensures you have met the required safety and competency standards.
2) Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Helmet and Eye Protection: Always wear a welding helmet with a proper filter lens to protect your eyes from radiation and sparks.
Protective Clothing: Wear flame-resistant clothing, gloves, and an apron to shield your skin from sparks and heat.
Respirators: Use a respirator to protect yourself from inhaling harmful fumes and gases.
3) Equipment Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular Checks: Inspect welding equipment regularly to ensure it is in good working condition. Look for damaged cables, loose connections, and other potential issues.
Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule to keep equipment functioning safely and efficiently.
4) Safe Work Environment:
Ventilation: Ensure your workspace is well-ventilated to disperse hazardous fumes and gases. Use local exhaust ventilation systems when necessary.
Fire Safety: Keep a fire extinguisher nearby and be aware of fire hazards in your work area. Remove flammable materials from the vicinity.
Workspace Organization: Keep your work area tidy and free from clutter to prevent accidents.
III. Advanced Safety Precautions
For those working in more specialized or hazardous welding environments, additional precautions are necessary.
1) Handling Hazardous Materials:
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS): Familiarize yourself with the MSDS for all materials you work with. These sheets provide critical information on handling, storage, and emergency measures.
Proper Storage: Store hazardous materials in appropriate containers and environments to prevent accidental exposure or reactions.
2) Advanced PPE:
Auto-Darkening Helmets: Invest in an auto-darkening welding helmet that adjusts the shade automatically, providing continuous protection.
High-Quality Respirators: Use advanced respirators, such as powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs), for maximum protection against fumes and gases.
3) Specialized Training:
High-Risk Environments: For welders working in high-risk environments, such as confined spaces or underwater, specialized training is crucial. This training should cover the unique hazards and safety procedures specific to these environments.
First Aid and Emergency Procedures: Ensure you are trained in first aid and know the emergency procedures for your workplace. Quick response can be critical in the event of an accident.
IV. Promoting a Safety Culture
Creating a culture of safety in the workplace is essential for long-term well-being. This involves not just individual responsibility but a collective commitment to safety practices.
1) Leadership and Commitment:
Management Support: Safety initiatives must be supported and enforced by management. This includes providing necessary resources and prioritizing safety in all operations.
Safety Officers: Appoint safety officers to oversee safety practices, conduct regular audits, and address any concerns promptly.
2) Continuous Education and Training:
Ongoing Training: Regularly update your skills and knowledge through ongoing training programs. This ensures you stay current with the latest safety standards and practices.
Workshops and Seminars: Participate in workshops and seminars on welding safety to learn from experts and share experiences with peers.
3) Reporting and Feedback:
Incident Reporting: Encourage the reporting of any safety incidents or near-misses. Analyzing these reports helps identify areas for improvement.
Feedback Mechanism: Implement a feedback mechanism where workers can suggest improvements or raise concerns about safety practices.
V. The Future of Welding Safety
As technology evolves, so do the tools and techniques for ensuring welding safety. Embracing innovation can lead to safer work environments and more efficient safety practices.
1) Technological Advancements:
Robotics and Automation: The use of robots in welding can significantly reduce the exposure of workers to hazardous conditions. Automation also ensures consistent quality and safety.
Advanced Monitoring Systems: Implementing advanced monitoring systems that track environmental conditions, equipment status, and worker health can preemptively address safety issues.
2) Research and Development:
New Materials: Research into new, safer welding materials can reduce the release of harmful fumes and gases.
Improved PPE: Continuous development of more effective personal protective equipment enhances safety without compromising comfort and efficiency.
3) Regulatory Changes:
Stricter Regulations: Governments and industry bodies are continuously updating safety regulations. Staying informed and compliant with these changes is essential for maintaining a safe work environment.
Global Standards: As the welding industry becomes more globalized, adopting international safety standards ensures consistent safety practices across borders.
IV. Conclusion
Welding safety is a multifaceted and dynamic field, requiring continuous effort and attention. By understanding the hazards, implementing essential safety tips, and staying abreast of technological and regulatory changes, welders can protect themselves and their colleagues from harm. As we look to the future, embracing innovation and fostering a culture of safety will ensure that welding remains a vital and secure profession.
Related articles
1. How to Prevent and Control Fire Hazards in Welding Operations?
2. 15 Tips for Improving Welding Safety
3. Controlling Hazardous Fume and Gases during Welding
4. Common Dangers of Welding and How to Avoid Them
5. When Light Poses Risks in Welding: Dangers and Solutions





