Welding is a critical process in various industries, from construction and automotive to shipbuilding and aerospace. Understanding the different welding positions and joint types is essential for producing high-quality welds. In this blog, we will explore the fundamental welding positions—1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, and 6G—and their respective joint types, providing you with the knowledge to enhance your welding skills and project outcomes.
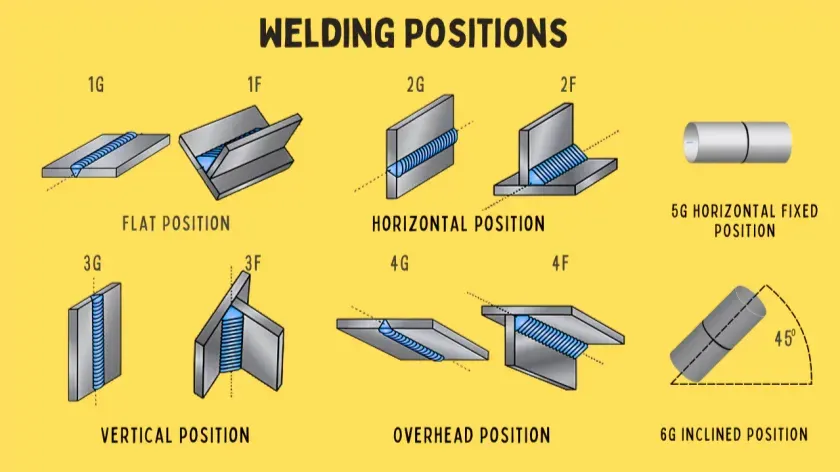
I. What Are Welding Positions?
Welding positions refer to the orientation of the weld and the workpiece in relation to the welder. These positions are standardized by the American Welding Society (AWS) and are crucial for certification and practical applications. Each position has unique challenges and requires specific techniques to achieve optimal results.
II. Understanding the Basic Welding Positions
1) 1G (Flat Position):
Description: The 1G position, also known as the flat position, is the simplest and most common welding position. The workpiece is placed horizontally, and the weld is performed on the upper side.
Application: This position is ideal for beginners due to its simplicity. It's commonly used in welding flat plates, pipelines, and simple structures.
Joint Types: Butt joints and fillet joints are commonly used in the 1G position.
2) 2G (Horizontal Position for Butt Welds):
Description: In the 2G position, the workpiece is vertical, and the weld is performed horizontally along the joint.
Application: This position is frequently used in pipeline welding and structural applications where horizontal welds are necessary.
Joint Types: T-joints and butt joints are typical for the 2G position.
3) 3G (Vertical Position)
Description: The 3G position involves welding in a vertical orientation. The weld can be performed either from bottom to top (uphill) or top to bottom (downhill).
Application: This position is essential for structural welding, especially in construction projects where vertical seams are common. Learn How to Weld Vertical: Tips and Techniques for Various Processes.
Joint Types: Butt joints and lap joints are commonly used in the 3G position.
4) 4G (Overhead Position)
Description: The 4G position requires welding from underneath the workpiece, which is positioned overhead.
Application: This challenging position is often encountered in repair work and in situations where the workpiece cannot be moved.
Joint Types: Overhead welding typically involves butt joints.
5) 5G (Horizontal Fixed Position)
Description: The 5G position is specifically for pipe welding. The pipe remains stationary, and the welder must perform the weld around the pipe's circumference.
Application: This position is critical in pipeline construction and maintenance, where pipes cannot be rotated.
Joint Types: Circumferential welds (girth welds) are typical in the 5G position.
6) 6G (Inclined Position)
Description: The 6G position is one of the most difficult welding positions. The pipe is inclined at a 45-degree angle, and the welder must weld around the pipe's circumference.
Application: This position is used for certifying welders due to its complexity. It's common in high-pressure and critical welding applications, such as oil and gas pipelines.
Joint Types: Circumferential welds are performed in the 6G position.
III. Why Are These Positions Important?
Understanding and mastering these welding positions is crucial for several reasons:
Certification: Many welding certifications require proficiency in specific positions. The 6G position, for example, is a standard test for many high-skill welding certifications.
Quality: Different positions impact the quality and strength of the weld. Mastering each position ensures that welds are strong, durable, and meet industry standards.
Versatility: Skilled welders who can work in various positions are highly sought after in the industry. This versatility opens up more job opportunities and projects.
IV. Conclusion
Mastering the various welding positions—1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, and 6G—is essential for any welder looking to advance their skills and career. Each position presents unique challenges and requires specific techniques to ensure high-quality welds. At Megmeet Welding Technology, we provide the tools and knowledge you need to excel in these welding positions, ensuring your projects are completed with precision and excellence.
Related articles:
1. Tips for Out-of-position Welding
2. What are the 4 Basic Welding Positions and How to Choose the Right One?
3. How welding defects (pores, undercuts) affect weld joint?
4. Welding Joint Types: Butt, Lap, Tee, Edge Joints & More.
5. Pipeline Vertical Welding Methods Basics and Precautions






